Technology has enabled us to exchange data rapidly. We don’t have to wait days to get data transferred from one medium to the other. Consider data in petabytes in one business unit of a company. If technology had not enabled us to move data in gigabytes, we would still be stuck with floppy disks and CDs, moving small chunks of data every day – which was a lot time consuming.
Same is the case with healthcare data. Around two decades ago, healthcare data was transferred from healthcare centers to insurance firms and brokerage houses through secured vehicles. All that data was in printed format and instead of AES 256 bit encryption, it was protected through lockers, safes, and file covers.
Only authorized personnel were allowed to carry medical records from one unit to the other or from one healthcare office to the brokerage firm. It was because the data included protected patient information (PPI) including the nature of disease, their bank details, SSN numbers and more.
In the wrong hands, that information could have caused privacy issues for the patients. The issue was that each hospital, healthcare unit, and medical center had its own format for storing and transporting their data. There was no standard process that ensured that the data was in compatible format and that only concerned persons were allowed access to it.
This changed with the introduction of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in 1996. HIPAA made sure that all healthcare data follows a certain standard.
In 2012, HIPAA rules were improved to include certain guidelines for proper data formats that could be exchanged between healthcare units, subsidiaries, and relevant insurance firms.
HIPAA ensured that administrative, medicare, and medicaid records were moved digitally instead of through in-hand and printable formats. Before 2012, HIPAA conducted many inquiries and found that 16,000+ patient records were not delivered using the standardized practices. There were over 70,000 patient complaints received by the organization about the mishandling of patient data by healthcare services. Some of the reasons behind complaints were data theft, impersonation, leading to improper patient insurance, and many more factors. This led HIPAA to take stringent measures for protection of patient data.
Now, healthcare services use a standard Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) format 837 for moving data from one unit/medical center to another or to a brokerage or insurance firm for the clearance of claims. Let’s learn about EDI 837 in detail below and read how it is bringing the healthcare industry on the data analytics forefront.
What does EDI Form Include? EDI 837 Data Structure
EDI formats are used for all types of data exchange in different industries. From medical to financial to construction,automobile, and retail, each industry uses different EDI formats to transfer data using data transfer protocols like FTP, HTTPS, IMAP, and others. The purpose of EDI is to transmit information to other companies electronically instead of using paper.
EDI 837 is specifically used for filing claims and for sending medical and healthcare data records to brokerage houses. Although a variety of business formats are used to transmit data, the HIPAA form 837 is one of the most common forms in healthcare. Today, not following HIPAA standards while transferring data can lead to violations of up to $1.5 million per year.
Format of EDI 837
Under the EDI 837 standard, the PPI format includes the following information.
- Description of the patient
- Condition for which the patient was treated
- Nature of service provided
- Total cost of the treatment
Division of EDI 837 Data Formats
EDI 837 data format is further segmented based on the nature of patient data. This practice was introduced to comply with HIPAA version 5010. It divides the 837 transaction set into three groups:
- 837P: This data is used for professional services offered to patients
- 837I: This data is for healthcare institutions, units, and medical centers
- 837D: This data involves dental practices.
Apart from healthcare units and medical centers, no other business unit can use EDI 837 data format even if it is linked to the healthcare industry. EDI data is sent by the providers to payers such as insurance companies, health maintenance organizations (HMOs), or government agencies such as Medicare, Medicaid, etc.
Health insurers and payers send payments and coordinate feedback through the EDI 835 transaction set – another EDI protocol that is used by brokerage firms for feedback to healthcare units. Both the EDI formats are made different to avoid mismanagement.
Industry Growth of Healthcare Data
In 2018, healthcare data was valued at $14.7 billion and it is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 20%. Owing to wider adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHR) the industry is estimated to reach $42 billion by 2024.
Similarly, environmental agencies have lobbied to reduce the use of papers to reduce environmental impact of paper-based communications. This lobbying will lead to more digital data in the healthcare sector in the years to come.
Today, mobile devices are being used to collect healthcare data such as heart rate, pulse rate, blood pressure, and much more. All this data needs to be converted in EDI format as some of this data is essential to patient health.
EDI 837 x12 Data Transfer Formats
Healthcare data is transferred through many formats. The following list includes some of the ways EDI 837 healthcare data is transferred from a healthcare unit to a brokerage house.
- Point-to-point EDI
- Web-based EDI
- EDI via AS/2
- EDI VAN
- Mobile EDI
Benefits of HIPAA & EDI 837 Format
- Before HIPAA standardization of data, patients were prone to data theft. HIPAA ensured that data fraud is prevented through EHR.
- Due to data corruption, patient information was often incorrect or incomplete. This would mean medical centers were not able to file a claim. Or if they did, the information was often rejected by the insurance firms due to insufficient data. EDI 837 Format ensures that the data remains encrypted while moving from source to destination.
- EDI 837 has streamlined many industry practices that were often mismanaged. As a result, payments are made within time, and efficiency of administrative functions has increased tremendously.
- HIPAA has imposed fine on unstandardized EDI data. For mismanagement of even one record, healthcare units are fined somewhere between $5,000 and $50,000. EDI 837 formats like HL7 and X12 reduce the occurrence of mishandling of patient data due to its structured format.
EDI 837 Guide: X12 vs HL7
EDI 837 x12 format is the standard format for exchanging information between healthcare partners. Mostly it is used for sending claims to insurance firms. The information is kept in x12 format and this makes it consistent, accurate, and easier to differentiate from HL7 EDI 837 format.

Source: HealthCaliber
EDi 837 HL7 format is used to exchange patient information between healthcare units, medical centers, and healthcare services so that if a patient moves from one city to the other, their data can be easily moved in an encrypted format to the other medical unit.
EDI 837 Data Mapping
EDI 837 data is transferred through multiple mediums to brokerage houses, insurance firms, and even shared across different business units of the same medical center. Most of the time, the destination doesn’t have the same infrastructure as that of source so the EDI 837 data needs to be converted to the destination file system. This is where data integration platforms come in. ata integration platforms allow EDI 837 data to be mapped to the destination system with drag and drop options.
There are many data formats in which EDI 837 data can be converted. But the most used ones are:
EDI 837 Guide: Mapping to Excel
EDI 837 data can be easily mapped to excel using source-to-target Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) mapping offered in a data integration software. The software offers connectors for multiple software and applications. EDI 837 connector moves data from the source system to the staging area. t is then converted into Excel format and loaded to the destination system.
EDI 837 Guide: Mapping to XML
In the similar way, data integration software allows EDI 837 data to be mapped to XML format. The data is first brought to the staging format and then relevant validation rules are applied to ensure that the XML file doesn’t lose any important patient information. Finally, it is moved to the destination system.
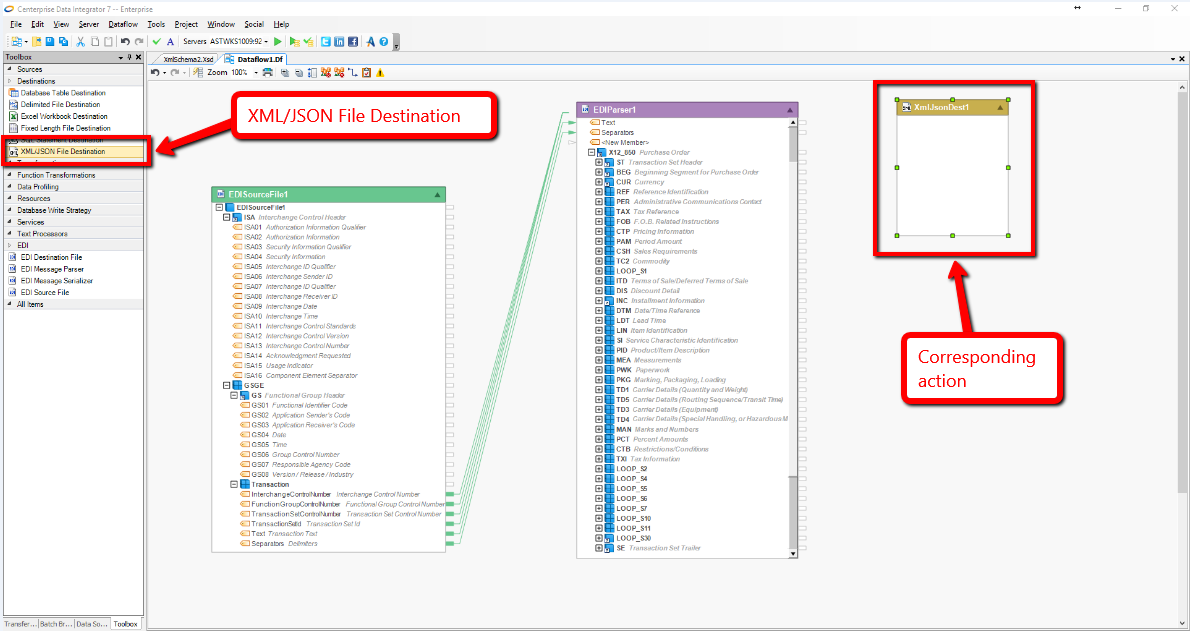
Source: Astera EDIConnect Blog
EDI 837 Guide: Mapping to JSON
Similarly, EDI 837 data can also be converted to JSON files. Most data integration software offer JSON file connectors for converting data from EDI 837 to JSON and back. They also offer data quality features which allow users to automatically transfer data to ensure completeness, timeliness, and accuracy.
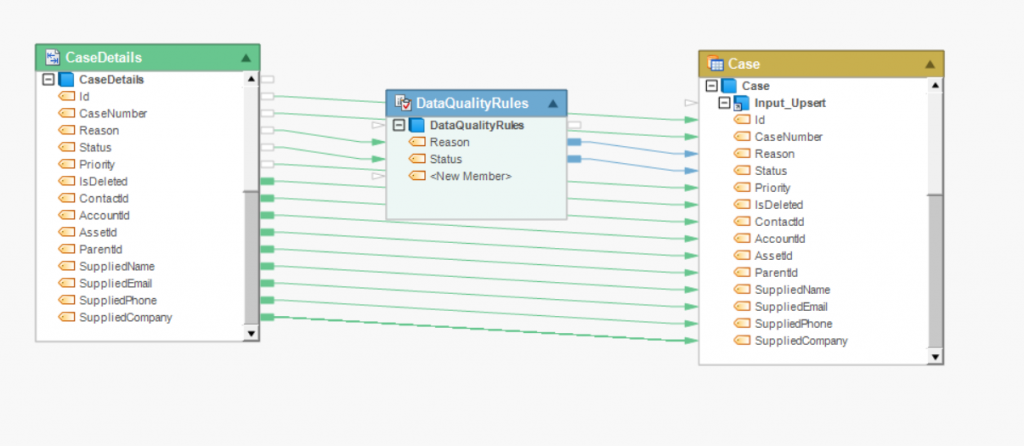
Source: Astera Healthcare Data Management
How Astera Centerprise Helps Integrate Healthcare EDI 837 Data?
Astera Centerprise data integration software offers over 40 connectors that allow it to convert EDI 837 data to any format. Since it is an ETL software it also offers a staging area where all data can be transformed from EDI 837 x12 and HL7 formats to destination formats. These can be XML, JSON, PDF, or any other for that purpose.
The conversion is performed in real-time and Astera Centerprise can convert thousands of data points within seconds through its parallel processing engine. Learn more about Astera Centerprise Data Integrator.